In this blog post, I’ll give an overview of ways to share Genome Browser data views with others.
Visualizing and sharing custom data is one of the most useful features of the UCSC Genome Browser tool. An independent review evaluating various genome browsers (http://tinyurl.com/genome-browsers), emphasized “the local and global exports for sharing sessions” is one of the site’s most “attractive functionalities,” with the report concluding that the UCSC Genome Browser “is the best tool of our evaluation from that point of view.”
Many veteran users are not aware of how easy it is to create and share browser views called sessions, especially using the more recent Public Sessions feature. Few users know that there are ways to modify URLs to share custom data, even to build URL links on top of data or sessions created by others. This blog post will give a wide overview of the many ways to share data on the Browser.
- TIP: You can watch a great introductory video to Saving and Sharing Sessions, which walks users through the steps to build a session and illustrates the new Public Sessions tool: http://bit.ly/sessionVid
SESSIONS AND PUBLIC SESSIONS
To access Sessions, under the top “My Data” menu there is a “My Sessions” option that leads to the page to create a URL snapshot of the view you are looking at in the Genome Browser. Once a user has created an account, on the Sessions Management page, they can then save a snapshot by giving the current view any “sessionName”. A link, built from the userName and given sessionName, will be created that can be shared with others: https://genome.ucsc.edu/s/userName/sessionName
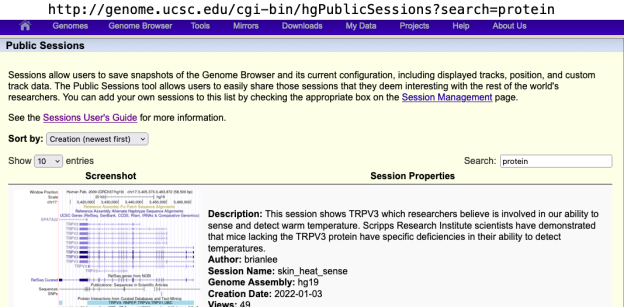
Once a session is created users have the option to click a “details” button on the Sessions Management page that leads them to an additional screen where they can enter a description. Newly created sessions are shareable by default, but can be made private (thereby requiring an account login to access), or they can be published to the Public Sessions page, where a search such as on the userName (https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgPublicSessions?search=userName) will bring up all sessions that the author published.
Public Sessions with descriptions are even more discoverable since matches will be returned on words found in the description. Public Sessions can be accessed under the “My Data” menu and a search term can be entered in the box on the right, or a URL can be built to scan for specific search terms as illustrated above for userName. If you search “protein” you will find all the sessions, for instance, that have mentioned protein in their description. Here’s an example: http://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgPublicSessions?search=protein
- TIP: When sessions are created with custom data uploaded, the uploaded data becomes “immortalized.” Usually any uploaded custom text-based tracks will be deleted in a few days, but by creating a session any uploaded tracks are marked as belonging to the associated userName account and attempts are made to preserve it. Please keep a local backup of your sessions contents, however, as the Browser is not a data storage service.
BUILDING URLS TO SET TRACK VISIBILITIES
Sometimes users want to hide all the tracks and only display certain data, and this can be done even without creating sessions. You can control the visibility of tracks from the URL with some of the following parameters:
- hideTracks=1 – hides all tracks
- <trackName>=hide|dense|pack|full – sets specified track or subtrack to a chosen visibilites
- <trackName>.heightPer=<###> – sets a bigWig track’s height to a particular number of pixels (between 20-100)
For example, you can use the following URL to hide every track (hideTracks=1), set the genome database to hg38 (db=hg38), set the mappability track to full visibility (mappability=full), and set the umap track height to 100 pixels (umap24Quantitative.heightPer=100): http://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTracks?db=hg38&hideTracks=1&mappability=full&umap24Quantitative.heightPer=100
BUILDING URLS TO CUSTOM TRACKS
Users can also share data with links without first creating a session by adding a “hgct_customText=” parameter to their base URL. For instance, if a group has data for the human hg38 database in a web-accessible location that meets the criteria for loading as a custom track, they can build URL links in this fashion: https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTracks?db=hg38&hgct_customText=http://location.online/dataFile
That online dataFile can be the track data, or a collection of more URLs to load more custom tracks. For instance, in a recent blog post about building bigBed tracks, https://bit.ly/UCSC_blog_bigBed, there was an example of hosting bigBed data at CyVerse. Since the data only displays in the position range of 1,405,000-1,448,000 on chromosome 5, a URL such as the below will load the hg19 genome (db=hg19) and go to a specific position (position=chr5:1405000-1448000) and then attach the remote file (hgct_customText=): https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTracks?db=hg19&position=chr5:1405000-1448000&hgct_customText=https://data.cyverse.org/dav-anon/iplant/home/brianlee/Lab_Primers.bigBed
- TIP: One advantage of not using sessions is that a user’s preexisting preferences for track displays will not be impacted. For instance, if they have a collection of clinical tracks displaying, using the hgct_customText= parameter or hubUrl= will add the new remote data to a user’s existing preferred clinical track configurations. Sessions, on the other hand, would disconnect existing remote data and change the position location as well as reconfigure tracks, to match everything saved when the session was created.
BUILDING URLS TO TRACK HUBS
Once a user has taken the step to build binary-indexed files such as bigBeds or bigWigs, they can go a step further and put their collection of tracks into a Track Hub. Track Hubs provide much more power for loading external data in more complex ways, such as enabling search indexes on uniquely named items in the remote data, or coloring tracks or individual elements.
Track Hubs are similar to the idea of having a text file that points to a collection of remotely hosted custom tracks. To make sharing easy, just one URL, called a hubUrl is given to the browser to load the Track Hub, and all the remotely hosted data, which must be in a binary-indexed format is then attached so only the data in the current view is transferred over the Internet. Here is a generic example of a link that would load hg38 track hub data: https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTracks?db=hg38?hubUrl=http://location/hub.txt
Here is a working example that loads onto the hg19 assembly (db=hg19) around a position (position=chr21:33,030,000-33,043,000) an example hub (hubUrl=): https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTracks?db=hg19&position=chr21:33,030,000-33,043,000&hubUrl=http://genome.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/help/examples/hubDirectory/hub.txt
- TIP: Once you start using URLs to share data instead of sessions, take caution to have only the first element use the question mark ? and then all other parameters to use the ampersand &, “?parameter1=value¶meter2=value¶meter3=value”. If you are having trouble, check to be sure that you have not confused the order of & and ? for your values.
BUILDING URLS TO TRACK HUBS ON ASSEMBLY HUBS
The UCSC Genome Browser provides a means to attach Track Hubs that can display novel genomes not hosted within the Browser. These are called assembly hubs. If a new assembly is being hosted remotely as an assembly hub, additional hub attachments also can be linked on top of that assembly hub, where the db= parameter is swapped with a genome= parameter as defined in the external assembly hub’s genomes.txt file (or genomes stanza when useOneFile is applied –see below).
In this following conceptual link, a genomeName is defined in an external assemblyHub.txt file that provides the Browser the underlying sequence of a declared genomeName. Then another collection of data, called hub.txt, is attached to that assembly hub, where that hub.txt is using the same genomeName in its genomes.txt file (or genome stanza). In the URL the very first parameter (genome=genomeName) tells the Browser that in one of these hubs there should be a similarly defined genome in order for the Browser to display the correct underlying sequence: https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTracks?genome=genomeName&hubUrl=http://location/assemblyHub.txt&hubUrl=http://location/hub.txt
- TIP: Note that hubUrl= can be used multiple times to attach multiple hubs, but only the genome=genomeName will inform the Browser which genome to display. The second hub.txt in this example can piggyback entirely on the first assemblyHub.txt to provide all the novel underlying genomeName sequence data.
Just to illustrate how complex the system can get, a further step could also add custom tracks to the Assembly Hub, which has a Track Hub attached simultaneously: https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTracks?genome=genomeName&hubUrl=http://location/assemblyHub.txt&hubUrl=http://location/hub.txt&hgct_customText=http://location.online/dataFile
ASSEMBLY HUB EXAMPLES WITH GenArk HUBS
The new GenArk assemblies come with quick links to load hubs from that collection. An example is https://genome.ucsc.edu/h/GCF_001984765.1, which will load the American beaver assembly (GCF_001984765.1). This short link is the equivalent of loading the hubUrl=https://hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/hubs/GCF/001/984/765/GCF_001984765.1/hub.txt and setting the genome=GCF_001984765.1 to the URL and pointing to the hgTracks CGI (the main Browser display). By condensing it all to this new short link format, we’ve attempted to make loading GenArk hubs easier.
- TIP: Once you start using URLs to define the Browser view, you will likely wish to reset the view occasionally. You can do this by going to the “Reset All User Settings” under the top “Genome Browser” menu. Another option is to directly point the browser to the cartReset CGI: https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/cartReset
These https://genome.ucsc.edu/h/GCF_### short links to GenArk assembly hubs can have additional parameters added to them, such as the following link that loads a custom track onto the GCF_001984765.1 assembly hub. The remote custom track in this example is a single bigBed hosted at CyVerse, where the URL is simultaneously setting the position to NW_017869957v1:1,437,578-1,648,889: https://genome.ucsc.edu/h/GCF_001984765.1?position=NW_017869957v1:1,437,578-1,648,889&hgct_customText=https://data.cyverse.org/dav-anon/iplant/home/brianlee/examples/GCF_001984765.1_C.can_genome_v1.0.cpgIslandExt.bb
A Track Hub can be attached to the Assembly Hub as seen in this version where the GCF_001984765.1assembly hub is redirected from the default position to NW_017869957v1:1,285,000-1,793,000 and the hubUrl= defines a CyVerse hosted hub.txt: https://genome.ucsc.edu/h/GCF_001984765.1?position=NW_017869957v1:1,285,000-1,793,000&hubUrl=https://data.cyverse.org/dav-anon/iplant/home/brianlee/examples/hub.txt
- TIP: Take a moment to look at this example hub.txt (https://data.cyverse.org/dav-anon/iplant/home/brianlee/examples/hub.txt). Note that it only has “
genome GCF_001984765.1” for the genomes stanza (since it is using useOneFile on and is also expecting to find a GenArk hub). It relies entirely on the GenArk assembly hub for the underlying assembly information.
Track Hubs loaded on Assembly Hubs are not limited to GenArk hubs. The GenArk hubs have special privileges because they have short links. If you try to attach any hub with something like “genome GCF_###” the Genome Browser will make an effort to find a match in the existing GenArk collection, and attach it automatically.
To illustrate how other assembly hubs outside of GenArk would work to have hubs attached, here is the longer version of the above link. In this case, the first hubUrl= is used to call out the location of this assembly hub, then the second hubUrl= is used again to load the second hub, and finally also hgct_customText comes into use to load a custom track
The point of these rather tortuous examples is that multiple groups can own the sources of the data. Everything after the base URL, https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTracks, can point to other places on the Internet with either the hubUrl= or hgct_customText= parameters. This means lab_X might have the assembly data, and lab_Y can generate a hub to view on that assembly, and lab_Z can further attach to those external groups even more custom data. And all this sharing and interoperability can happen without ever creating session links.
BUILDING URLS ATTACHING TRACK HUBS AND CUSTOM TRACKS TO SESSIONS
Using sessions is powerful since it lets you customize your view of the Genome Browser. Users can create a session (or borrow another from the Public Session page) and use that session’s userName and sessionName to attach their own custom data.
- Here is a model link for attaching custom tracks: https://genome.ucsc.edu/s/userName/sessionName?hgct_customText=http://location.online/dataFile
- Here is a model link for attaching track hubs: https://genome.ucsc.edu/s/userName/sessionName?hubUrl=http://location.online/hub.txt
This can have the advantage of creating shorter links or also preconfiguring the browser to a certain position or display. We recently added the ability to customize the font on the Browser so a session can even be used just as a different way of viewing the same data stylistically, for instance making the display easier for you to read.
Here are some real-world examples borrowing from real Public Sessions. To load on a Public Session, go to the “My Data” menu, then choose “Public Sessions”, and then you can click on the image of any session to load it. You can build your own URL from an existing Public Session by noting the Author field (equivalent to the session’s source userName) and the Session Name field, like so: https://genome.ucsc.edu/s/userName/sessionName
- TIP: Session names will URL encode whitespace or other special characters, where any spaces in the name would become %20 (My%20session%20name), this is one reason using underscores (or camelCase) instead of spaces in your sessionNames makes for cleaner links.
Here’s a session on hg19 that will load and also attach the earlier CyVerse custom track: https://genome.ucsc.edu/s/brianlee/AvantG_Font?position=chr5:1405000-1448000&hgct_customText=https://data.cyverse.org/dav-anon/iplant/home/brianlee/Lab_Primers.bigBed
Here’s one that will load a few hubs on a session that points to hg38 and also opens the display to the SIRT1 gene using the &singleSearch=knownCanonical&position=SIRT1 parameters: https://genome.ucsc.edu/s/brianlee/Times_Font?hubUrl=http://fantom.gsc.riken.jp/5/datahub/hub.txt&hubUrl=http://expdata.cmmt.ubc.ca/JASPAR/UCSC_tracks/hub.txt&hubUrl=http://remap.univ-amu.fr/storage/public/hubReMap2020UCSC/hub.txt&singleSearch=knownCanonical&position=SIRT1
Again, these complex links are to illustrate that there are multiple ways to view multiple groups of data across the world in the Genome Browser. You can get to the data either through clicks and searches on the website or by building Sessions or Public Sessions and URL links to remotely hosted data. This blog post could not cover every topic but gives a good introduction to the ways to share data with sessions or complex URLs. To learn more about links, see these documentation pages:
- http://genome.ucsc.edu/FAQ/FAQlink.html
- http://genome.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/help/customTrack.html#optParams
- TIP: If you love modifying URLs, click on the “example links” in the second #optParams section above to see how you can even add parameters like highlight= to define multiple colored vertical highlights.
Links to guides for Sessions, Track Hubs, Custom Tracks, and videos can be found on our training page:
This entry written by Brian Lee. If after reading this blog post you have any questions, please email genome@soe.ucsc.edu. All messages sent to that address are archived on a publicly accessible forum. If your question includes sensitive data, you may send it instead to genome-www@soe.ucsc.edu.